Cats
Cats experience a variety of skin and ear conditions that can cause itching, hair loss, infections, and discomfort. Many of these issues are similar to those seen in dogs but require different approaches due to feline-specific physiology and behavior. Veterinary dermatologists specialize in diagnosing and treating these complex problems with precision and care.
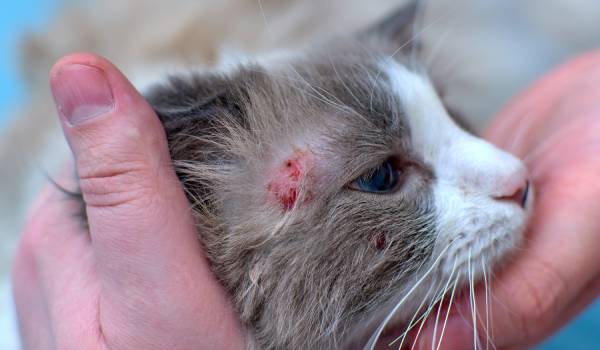
Allergies in Cats
Allergies are among the most common causes of itching, scratching, and skin infections in cats. Unlike dogs, cats often show more subtle signs such as overgrooming or hair loss, which can make diagnosis challenging.
There are three main types of allergies in cats:
- Flea Allergy Dermatitis (FAD): This is the most common allergic reaction in cats. Even a few flea bites can cause severe itching. Fleas are often difficult to detect on cats, making consistent flea control vital. Veterinary dermatologists can recommend the best flea prevention products and strategies tailored for cats.
- Food Allergies: Food hypersensitivity in cats can lead to chronic itching and gastrointestinal symptoms. Identifying food allergies requires carefully supervised elimination diets, often lasting several weeks. Only by removing suspected ingredients and monitoring the response can a diagnosis be confirmed.
- Environmental Allergies: Cats can be allergic to pollen, dust mites, molds, and other environmental allergens. Diagnosing these allergies involves specific testing. Treatment may include allergen avoidance, medications to control symptoms, and in some cases, allergen-specific immunotherapy (“allergy shots”) to desensitize the cat over time.
Veterinary dermatologists have the specialized training to perform and interpret these tests correctly. Misdiagnosis or incomplete diagnosis often leads to treating symptoms only, rather than the root cause, which can result in long-term medication use with associated costs and potential side effects.
Skin Infections and Parasites
Secondary skin infections are common in allergic cats due to constant scratching and self-trauma. These infections are typically caused by bacteria such as Staphylococcus species or yeast like Malassezia. Treating the infection is essential, but without addressing the underlying allergy, infections tend to recur.
Cats are also susceptible to parasitic infestations which cause significant itching and discomfort:
- Ear Mites (Otodectes cynotis): These tiny parasites are common in cats and cause ear infections characterized by dark discharge, shaking, and scratching at the ears. Veterinary dermatologists use ear swabs and microscopic examination to diagnose and treat these infections effectively.
- Cheyletiella Mites (“Walking Dandruff”): These surface mites cause flaky skin and mild itching. Diagnosis requires a thorough skin scrape or tape test.
- Demodex Mites: Though rare in cats compared to dogs, demodicosis can occur and causes patchy hair loss and scaling. Diagnosis is made by deep skin scrapings.
Proper parasite control is critical to reducing discomfort and preventing secondary infections.
Alopecia and Hair Loss
Hair loss, or alopecia, in cats can be caused by a range of factors, including infections, parasites, allergies, and hormonal imbalances.
- Self-Induced Alopecia: Often due to excessive grooming triggered by itching or stress, cats may develop bald patches. This condition, called psychogenic alopecia, can be difficult to manage without identifying and addressing the underlying cause.
- Infections and Parasites: As noted, bacterial, fungal, or parasitic infections can cause hair loss. Veterinary dermatologists will perform tests such as skin scrapings, fungal cultures, or biopsies to identify the cause.
- Hormonal Diseases: Conditions such as hyperthyroidism or other endocrine disorders may present with hair thinning or patchy hair loss.
Veterinary dermatologists have the experience to differentiate between these causes and create a tailored treatment plan.
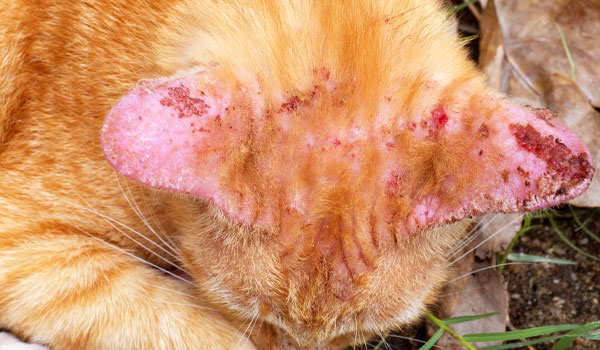
Ear Disorders
Ear problems are a frequent complaint in cats. In addition to ear mites, cats may suffer from bacterial or yeast infections, allergic reactions, and inflammatory conditions.
Symptoms include shaking of the head, scratching at the ears, redness, swelling, and discharge. These can cause significant discomfort and may lead to chronic issues if untreated.
Veterinary dermatologists use otoscopic exams, cytology, and cultures to diagnose the problem accurately and prescribe appropriate treatments such as topical medications, systemic antibiotics, or anti-inflammatory drugs.
Tumors, Lumps, and Cysts
Cats can develop lumps and bumps on their skin that vary from benign cysts to malignant tumors. Veterinary dermatologists are skilled at identifying, diagnosing, and treating these growths.
Early detection and diagnosis are important to ensure the best outcome. This may involve fine needle aspiration, biopsies, or surgical removal depending on the type and location of the lesion.
Autoimmune and Immune-Mediated Skin Diseases
Although less common, cats can suffer from autoimmune skin diseases where the body’s immune system attacks healthy skin cells. Examples include pemphigus foliaceus and lupus erythematosus.
These conditions often require specialized diagnosis through skin biopsies and careful management with immunosuppressive medications.
Veterinary dermatologists have the knowledge and experience to manage these complex diseases effectively.
Why Choose a Veterinary Dermatologist for Your Cat?
Skin and ear conditions in cats can be frustrating to manage and may not respond well to standard treatments. Veterinary dermatologists have advanced training and access to specialized diagnostic tools, allowing them to uncover the underlying causes of chronic problems and develop effective, long-term treatment plans.
By working with a specialist, you can help your cat live more comfortably and reduce the need for ongoing medications or repeated veterinary visits.


